Industrial automation is transforming how industries operate, making processes faster, more efficient, and highly reliable. At the core of this revolution are motors. Motors power machines, drive automation systems, and ensure precision in manufacturing processes. From conveyors to robotic arms, motors are essential for achieving the level of accuracy and efficiency required in modern industries.
In this blog, we will explore the role of motors in precision industrial automation, the different types of motors used, their applications, benefits, and how they shape the future of smart manufacturing.
What Are Industrial Motors?
Motors are components that convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. In industrial automation, they act as the driving force behind machines, tools, and automated systems. They provide the motion needed for moving parts, rotating equipment, and powering operations that demand precision and consistency.

Without motors, automation would not exist. From simple pumps to advanced robotic systems, motors make it possible to achieve high productivity while maintaining quality standards.
Why Are Motors Important in Precision Automation?
Precision industrial automation requires accurate, repeatable, and reliable motion control. Motors enable this by:
- Providing consistent power: Motors deliver continuous torque and speed to keep automation systems stable.
- Ensuring precision: With modern control systems, motors can achieve high accuracy in movement.
- Enhancing efficiency: Motors help reduce energy waste by operating only when required and at optimized speeds.
- Supporting flexibility: They can be adapted to different industrial applications, from packaging to assembly lines.
In short, motors are the backbone of automation systems that rely on precision and reliability.
Types of Motors Used in Industrial Automation
Different types of motors are designed to meet the needs of various applications in automation. Let’s look at the most common ones:
1. AC Motors
AC (Alternating Current) motors are widely used in industrial applications because of their durability and cost-effectiveness. They are suitable for applications where continuous operation is required.
Induction Motors: Common in pumps, fans, and conveyors.
Synchronous Motors: Used where constant speed is essential, such as in robotics and CNC machines.
2. DC Motors
DC (Direct Current) motors provide excellent speed control and torque. They are ideal for applications requiring precision and variable speed.
Brushed DC Motors: Simple and cost-effective, often used in small automation systems.
Brushless DC Motors (BLDC): More efficient and durable, widely used in robotics and precise positioning systems.
3. Servo Motors
Servo motors are designed for high-precision applications. They provide accurate control of angular position, velocity, and acceleration. Common in robotics, CNC machinery, and packaging systems.
4. Stepper Motors
Stepper motors move in small, precise steps. They are excellent for tasks requiring exact positioning, such as 3D printing, robotic arms, and medical devices.
5. Linear Motors
Unlike rotary motors, linear motors provide direct linear motion without conversion mechanisms. They are used in applications like semiconductor manufacturing and high-speed conveyors.
Key Roles of Motors in Precision Automation
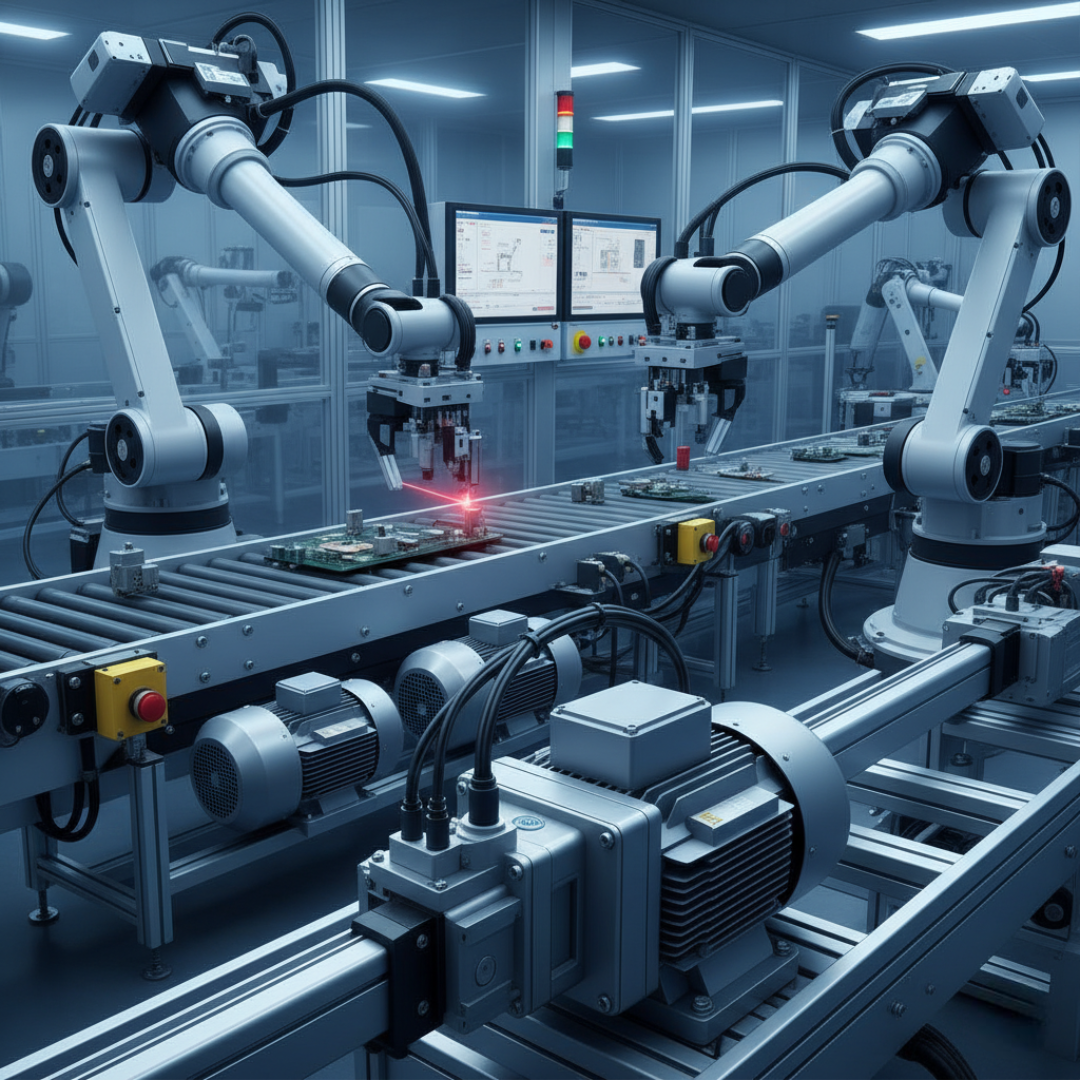
Motors are not just about providing motion—they play multiple roles in ensuring precision, reliability, and efficiency. Let’s break it down:
1. Precision Motion Control
Motors ensure that machines move exactly as required. Whether it’s a robotic arm assembling delicate components or a conveyor transporting goods, motors make sure every movement is accurate and repeatable.
2. Energy Efficiency
Modern motors are designed with energy-saving technologies. Variable frequency drives (VFDs) and smart controls allow motors to adjust their speed and torque according to demand, reducing energy consumption.
3. Flexibility in Applications
Motors can be customized for a wide range of applications. From high-speed manufacturing to heavy-load lifting, motors can adapt to different needs while maintaining precision.
4. Reliability and Durability
Industrial environments are harsh, but motors are built to withstand extreme conditions while delivering consistent performance. This reliability reduces downtime and increases productivity.
5. Integration with Automation Systems
Motors integrate effortlessly with sensors, controllers, and programmable logic controllers (PLCs). This allows industries to create smart automation systems that respond to real-time data.
Applications of Motors in Industrial Automation
Motors are used across a wide range of industries and automation systems. Here are some key applications:
1. Manufacturing Industry
- Operating conveyors and assembly lines.
- Driving robotic arms for welding, painting, and assembly.
2. Food and Beverage Industry
- Motors in packaging machines ensure accurate filling, sealing, and labeling.
- Conveyor belts powered by motors help in sorting and transporting products.
3. Automotive Industry
- Motors power robotic arms used in car assembly.
- Used in automated inspection systems for quality control.
4. Textile Industry
- Motors drive weaving machines, spinning equipment, and cutting tools.
- Automation ensures uniformity and high-quality textile production.
5. Pharmaceutical Industry
- Motors in dosing and filling machines maintain precision in medicine packaging.
- Stepper and servo motors ensure accuracy in labeling and sorting.
6. Logistics and Warehousing
- Motors operate automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and conveyor systems.
- Enable high-speed sorting in large distribution centers.
Benefits of Motors in Precision Automation
Using motors in industrial automation brings numerous advantages:
- High Accuracy: Motors ensure exact positioning and controlled movement.
- Consistency: Machines powered by motors deliver the same output repeatedly.
- Productivity: Motors increase speed and efficiency, reducing manual intervention.
- Safety: Automation with motors minimizes human involvement in hazardous environments.
- Scalability: Motors support automation systems of all sizes, from small equipment to large industrial plants.
Motors and Smart Automation
With Industry 4.0, motors are becoming smarter. Bright motors can now communicate with other devices, collect performance data, and optimize their operations in real-time.
Key Features of Smart Motors:
- IoT Connectivity: Motors connected to the Internet of Things (IoT) can be monitored remotely.
- Predictive Maintenance: Sensors in motors detect early signs of wear, preventing breakdowns.
- Energy Monitoring: Smart motors provide data on energy consumption, helping industries optimize costs.
Challenges in Motor Applications
While motors are vital, industries face some challenges:
- Energy Consumption: Motors account for a large portion of industrial energy use.
- Maintenance Needs: Motors require regular inspection and servicing.
- Initial Investment: High-quality motors with advanced features can be expensive.
- Integration Complexity: Combining motors with advanced automation systems requires skilled expertise.
Industries address these challenges by adopting energy-efficient motors, predictive maintenance tools, and proper training for workers.
The Future of Motors in Precision Automation
The role of motors will only expand as industries demand greater precision and efficiency. Future trends include:
- AI-Powered Control Systems: Artificial intelligence will optimize motor performance automatically.
- More Compact Motors: Miniaturized motors for small-scale precision tasks.
- Eco-Friendly Motors: Focus on sustainability with energy-efficient and recyclable designs.
- Advanced Robotics: Motors will drive next-generation robots capable of performing highly complex tasks with human-like precision.
Motors are the backbone of precision industrial automation. From driving simple conveyors to powering advanced robotics, they ensure accuracy, reliability, and efficiency in industrial processes. As industries embrace smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0, motors will play an even greater role in shaping the future of automation. By integrating advanced motors into automation systems, businesses can achieve higher productivity, reduce operational costs, and maintain competitive advantage in today’s fast-paced industrial world.

